The relative rate at which the price of a security moves up and down. Volatility is found by calculating the annualized standard deviation of daily change in price. If the price of a stock moves up and down rapidly over short time periods, it has high volatility. If the price almost never changes, it has low volatility. n other words, volatility refers to the amount of … [Read more...]
Measuring Stock Market Volatility
Measuring the S&P 500 on the VIX The composition of the VIX was changed in 2003. At that time, the CBOE created a "new" VIX by making two changes to the original version. First, options on the S&P 500 index were substituted for those on the S&P 100. The CBOE decided that the S&P 500 — a widely followed average commonly used by mutual funds as a benchmark … [Read more...]
VIX & Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE)
The ticker symbol for the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) Volatility Index, which shows the market's expectation of 30-day volatility. It is constructed using the implied volatilities of a wide range of S&P 500 index options. This volatility is meant to be forward looking and is calculated from both calls and puts. The VIX is a widely used measure of market risk and … [Read more...]
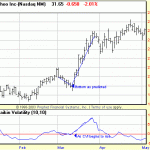
Chaikin Volatility Indicator
The Chaikin Volatility Indicator uses the percent change of two moving averages of a volume weighted accumulation-distribution line to determine the volatility of a financial data series. Chaikin quantifies volatility as a widening of the range between the high and the low price of a security. This does not take trading gaps into account as Average True Range does. As shown … [Read more...]