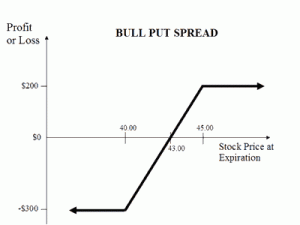
A type of options strategy that is used when the investor expects a moderate rise in the price of the underlying asset. This strategy is constructed by purchasing one put option while simultaneously selling another put option with a higher strike price. The goal of this strategy is realized when the price of the underlying stays above the higher strike price, which causes the short option to expire worthless, resulting in the trader keeping the premium.
The maximum possible profit using this strategy is equal to the difference between the amount received from the short put and the amount used to pay for the long put. The maximum loss a trader can incur when using this strategy is equal to the difference between the strike prices and the net credit received. Bull put spreads can be created with in-the-money or out-of-the-money put options, all with the same expiration date.
Limited Upside Profit
If the stock price closes above the higher strike price on expiration date, both options expire worthless and the bull put spread option strategy earns the maximum profit which is equal to the credit taken in when entering the position.
The formula for calculating maximum profit is given below:
- Max Profit = Net Premium Received – Commissions Paid
- Max Profit Achieved When Price of Underlying >= Strike Price of Short Put
When to use
A Put Bull Spread has the same payoff as the Call Bull Spread except the contracts used are put options instead of call options. Even though bullish, a trader may decide to place a put spread instead of a call spread because the risk/reward profile may be more favourable. This may be the if the ITM call options have a higher implied volatility than the OTM put options. In this case, a call spread would be more expensive to initiate and hence the trader might prefer the lower cost option of a put spread.